1.3. Run calculation command: qha run¶
Table of contents:
1.3.1. How to write computational settings file¶
First one needs to prepare a standard input file and a YAML file specifying
the computational settings, which is referred to settings.yaml here.
Please refer to this website
if not familiar with YAML syntax.
Here are the keys that can be recognized in settings.yaml:
calculation: The calculation type user wants to perform. Allowed values aresingle,same phonon dosanddifferent phonon dos.NT: Number of temperatures on the gridT_MIN: Desired minimum temperature to calculate, in Kelvin, default value is 0 K.DT: The interval between two nearest temperatures on the gridNTV: Number of volumes (or equivalently, pressure) on the girdDELTA_P: The interval between two pressures on the grid, the default value is \(0.1\) GPaDELTA_P_SAMPLE: Pressure-sampling interval, used for output, the default value is \(1\) GPaP_MIN: Desired minimum pressure to calculate, in GPainput: Name(s) of the input file(s).In the single-configuration calculation, only the path of the file is needed,
In the multi-configuration calculation, the names of the inputs files and the corresponding configuration degeneracy are given in a YAML dictionary syntax.
static_only: Whether to include the vibrational contribution in the calculation. Allowed values areTrue(not include) orFalse(include, default).order: Order of Birch–Murnaghan equation of state fitting, can be3(default),4or5.energy_unit: Energy unit in the output file can bery(default) orevthermodynamic_properties: Which thermodynamic properties will be calculated byqha. Allowed values areF: the Helmholtz free energyG: the Gibbs free energyU: the internal energyH: the enthalpyV: the volumeCp: the isobaric heat capacityCv: the volumetric heat capacityBt: the isothermal bulk modulusBtp: the derivative of the isothermal bulk modulus with respect to pressureBs: the adiabatic bulk modulusalpha: the thermal expansion coefficientgamma: the Grüneisen parameter
target: The default value isparallel. This is a Numba package option. Allowed options arecpu(used on single-threaded CPU),parallel(used on multi-core CPU), andcuda(used on CUDA GPU). See its official documentation for help.results_folder: The path to store all calculated values, the default value is./results, which is a directory named results in the same folder as theinputfile.T4FV: Temperature for \(F(T_i, V)\) plotting. By default is['0', '300'].high_verbosity: Two verbosity levels are implemented in the output file,TrueorFalse(default).
1.3.2. How to make input data¶
The input format is as below:
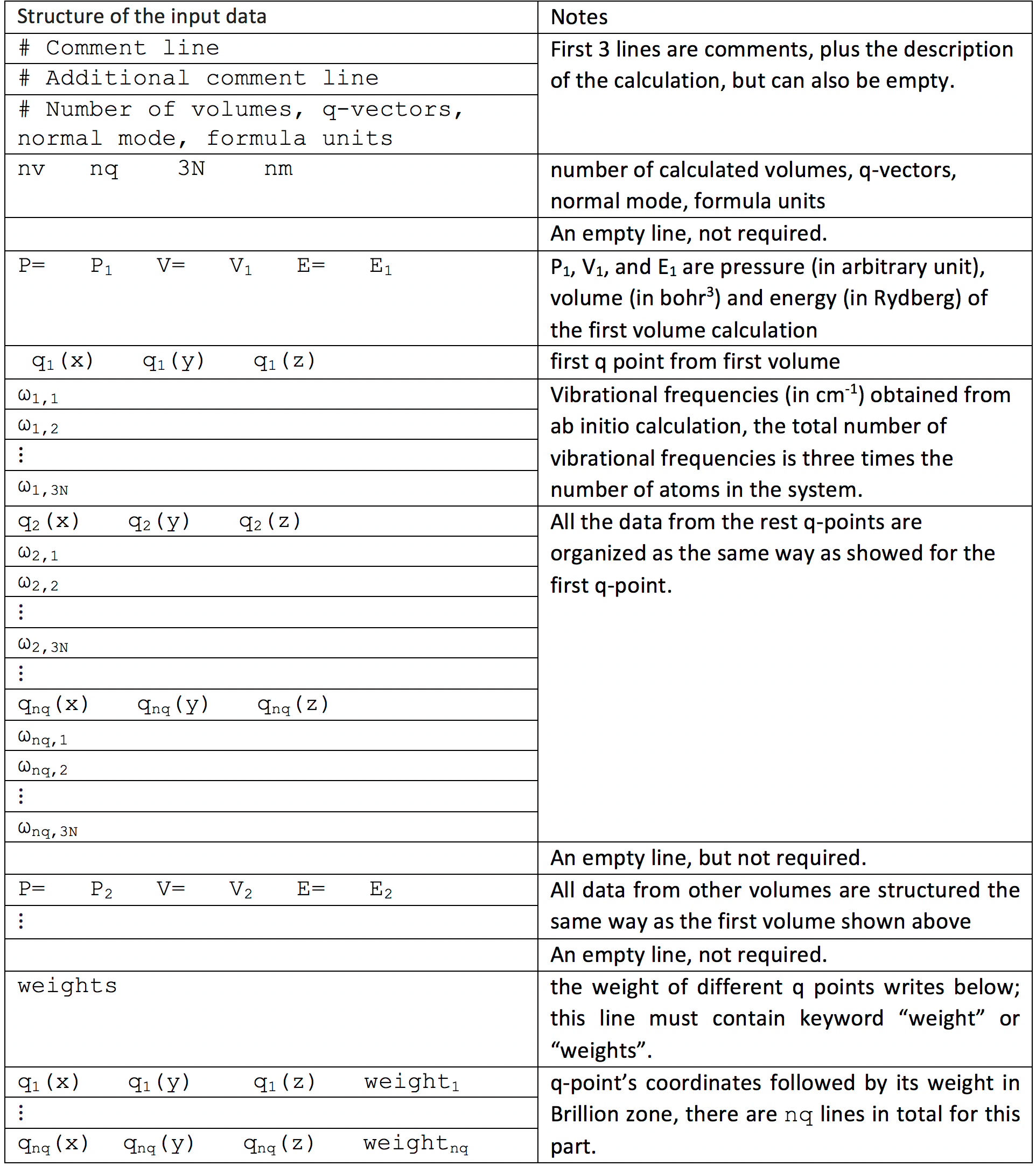
After one has prepared settings.yaml and input in the same directory,
just open the terminal, redirect to that directory and run:
$ qha run ./settings.yaml
then the results will be generated in the directory specified
in results_folder option in settings.yaml.
If the settings.yaml is not in the same directory as the input file, one has to explicitly specify the
path of it on his/her computer.
1.3.3. Output¶
The output files’ names and their meanings are as below:
Helmholtz free energy:
f_tp_ry.txtorf_tp_ev.txtGibbs free energy:
g_tp_ry.txtorg_tp_ev.txtEnthalpy:
h_tp_ry.txtorh_tp_ev.txtVolume:
v_tp_bohr3.txtorv_tp_ang3.txtPressure-specific heat capacity:
cp_tp_jmolk.txtVolume-specific heat capacity:
cv_tp_jmolk.txtIsothermal bulk modulus:
bt_tp_gpa.txtDerivative of the isothermal bulk modulus with respect to pressure:
btp_tp.txtAdiabatic bulk modulus:
bs_tp_gpa.txtThermal expansion:
alpha_tp.txtThermal Grüneisen parameters:
gamma_tp.txt